
This is an important factor in understanding how changes in ventilation or perfusion can impact arterial or end-tidal gases.

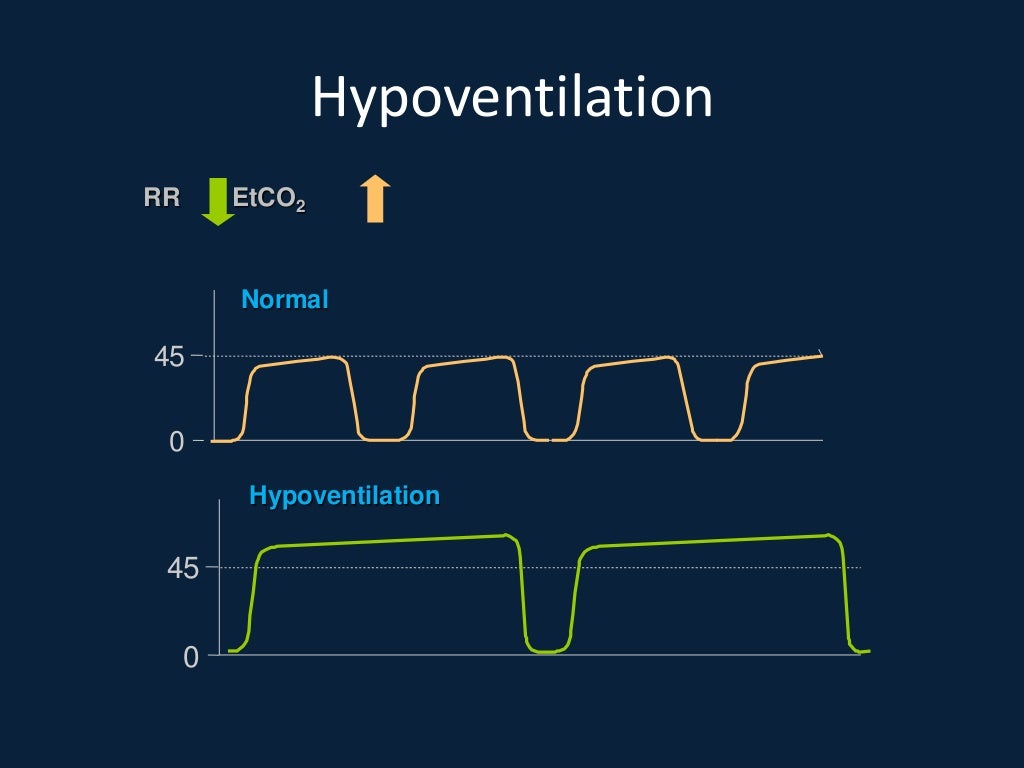
1 Therefore, within each alveolar unit, CO 2 equilibrates sooner than O 2. As much CO 2 is exchanged for a partial pressure difference of 5 mmHg between mixed venous and alveolar space as O 2 is exchanged when the partial pressure difference is 60 mmHg. The diffusion properties of CO 2 are greater than those of oxygen as a result the equilibration between the mix-venous capillary and alveolar compartments occurs sooner during transit of blood through the alveolar unit. These diffusion gradients result in equilibration through the alveolar unit (Figure 1). For CO 2, the opposite exists: the mixed venous partial pressure of CO 2 is greater than within the alveoli. Under normal gas exchange, the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveolus is greater than within the mixed venous circulation. As the capillary blood traverses the alveolar unit, gas exchange occurs so that equilibration of gases occurs at the end-capillary portion of the alveolar unit. As oxygen enters an alveolar unit during inhalation, mixed venous blood enters through capillaries that originate from the pulmonary artery. In contrast, the atmospheric concentration of CO 2 is negligible (FiCO 2 = ~0%). But with supplemental oxygen, the FiO 2 can be increased to 40% or higher with use of nasal prongs, a face mask, or forms of mechanical ventilation. Under medical care, the minimal FiO 2 that can be delivered is room air (FiO 2=21%). The air we breathe contains 21% oxygen and is commonly denoted as the fractional inspired oxygen concentration (FiO 2). In contrast, when respiratory failure is imminent, ventilation decreases and is reflected by increasing PCO 2 and etCO 2 values. For instance, under respiratory distress, where ventilation is rapid and deep, the amount of CO 2 cleared during exhalation increases, and this is reflected as low PCO 2 and low etCO 2. Changes to lung ventilation that become clinically significant are commonly identified through these measurement modalities. Abnormalities affecting carbon dioxide are assessed via measurements of partial pressures within the circulation (i.e. The metabolic byproduct of tissue metabolism is carbon dioxide (CO 2), which is transported from the tissue via blood circulation and is removed during exhalation. For example, both stroke and myocardial infarction involve tissue necrosis as a direct result of tissue hypoxia resulting from obstructed blood flow.

When tissue is exposed to anaerobic conditions for prolonged periods, tissue necrosis may ensue. under anaerobic conditions), the metabolic processes become hampered, and alternative fuel sources are utilized to generate ATP. This energy is more commonly referenced as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The reason is that the conversion of glucose, the dominant fuel for cells, requires a high amount of oxygen to produce energy the body can utilize. Oxygen is central to the proper functioning of the human body, which functions optimally under aerobic conditions. This paper provides an overview of the key steps along this path.
#Normal end tidal co2 kpa series
Oxygenation involves a series of steps that include inhalation, gas exchange, oxygen transport, oxygen delivery, oxygen extraction and exhalation. Oxygen transport Oxygen Utilization BasicsĪn exploration of the utility of respiratory gas measurement starts with an understanding of the basics of oxygenation and oxygen transport.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
